In this example we look at the enviro:bit which is an add on from pimoroni which has a BME280 temperature, pressure, and humidity sensor fitted to it a long with a TCS3472 light and colour sensor and a MEMS microphone
Lets look at the enviro:bit fitted to a bpi:bit
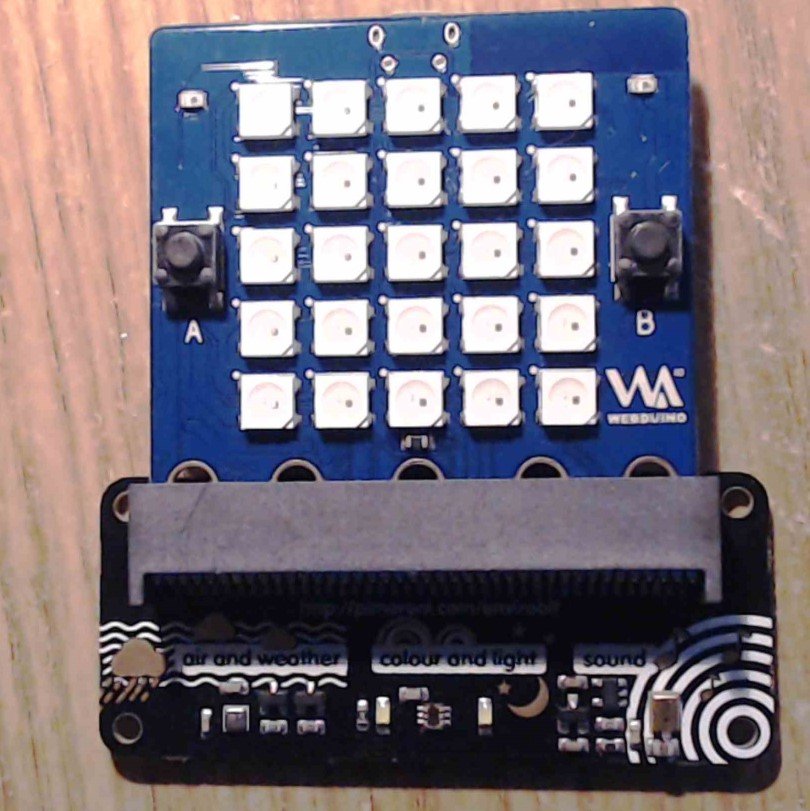
enviro:bit and bpi:bit
Features:
- Comes fully-assembled and ready to use.
- BME280 temperature, pressure, and humidity sensor.
- TCS3472 light and colour sensor.
- MEMS microphone.
- Compatible with micro:bit.
- Microsoft MakeCode and MicroPython support.
- No soldering required!
Lets look at the TCS34725
The TCS3472 device provides a digital return of red, green, blue (RGB), and clear light sensing values. An IR blocking filter, integrated on-chip and localized to the color sensing photodiodes, minimizes the IR spectral component of the incoming light and allows color measurements to be made accurately.
The high sensitivity, wide dynamic range, and IR blocking filter make the TCS3472 an ideal color sensor solution for use under varying lighting conditions and through attenuating materials. This data is transferred via an I2C to the host.
Features
- Integrated IR blocking filter
- 3.8M:1 dynamic range
- Four independent analog-to-digital converters
- A reference channel for color analysis (clear channel photodiode)
Benefits
- Minimizes IR and UV spectral component effects to produce accurate color measurement
- Enables accurate color and ambient light sensing under varying lighting conditions
- Minimizes motion/transient errors
- Clear channel provides a reference which allows for isolation of color content
Parts List
| Name | link |
| Banana PI Bit board | Banana PI Bit board with EPS32 |
| envirobit | Pimoroni enviro:bit for BBC micro:bit |
Code
You need to import the adafruit TCS34725 library – you can add this via the library manager
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Adafruit_TCS34725.h"
/* Initialise with default values (int time = 2.4ms, gain = 1x) */
// Adafruit_TCS34725 tcs = Adafruit_TCS34725();
/* Initialise with specific int time and gain values */
Adafruit_TCS34725 tcs = Adafruit_TCS34725(TCS34725_INTEGRATIONTIME_700MS, TCS34725_GAIN_1X);
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (tcs.begin()) {
Serial.println("Found sensor");
} else {
Serial.println("No TCS34725 found ... check your connections");
while (1);
}
// Now we're ready to get readings!
}
void loop(void) {
uint16_t r, g, b, c, colorTemp, lux;
tcs.getRawData(&r, &g, &b, &c);
colorTemp = tcs.calculateColorTemperature(r, g, b);
lux = tcs.calculateLux(r, g, b);
Serial.print("Color Temp: ");
Serial.print(colorTemp, DEC);
Serial.print(" K - ");
Serial.print("Lux: ");
Serial.print(lux, DEC);
Serial.print(" - ");
Serial.print("R: ");
Serial.print(r, DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("G: ");
Serial.print(g, DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("B: ");
Serial.print(b, DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("C: ");
Serial.print(c, DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(" ");
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open the serial monitor window and you will see something like this
Color Temp: 7173 K – Lux: 11 – R: 31 G: 26 B: 26 C: 39
Color Temp: 5645 K – Lux: 14 – R: 41 G: 32 B: 31 C: 53
Color Temp: 5153 K – Lux: 30 – R: 80 G: 63 B: 59 C: 103
Color Temp: 4887 K – Lux: 36 – R: 94 G: 74 B: 68 C: 133
Color Temp: 5310 K – Lux: 23 – R: 60 G: 48 B: 45 C: 93
Color Temp: 4981 K – Lux: 42 – R: 113 G: 88 B: 82 C: 167
Color Temp: 5565 K – Lux: 274 – R: 834 G: 633 B: 620 C: 974
Color Temp: 5653 K – Lux: 261 – R: 822 G: 618 B: 611 C: 937